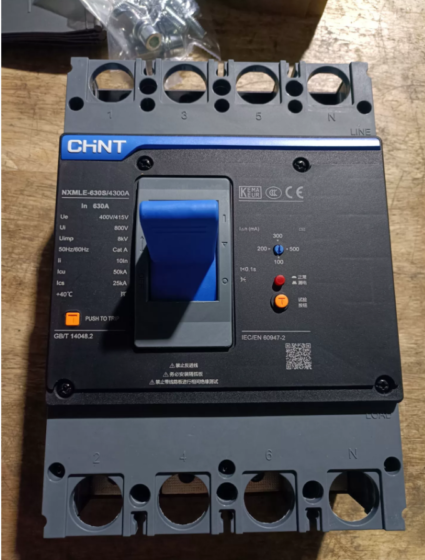
CHINT NXM250S/3200 200A” is the complete model number of a disjoncteur à boîtier moulé (MCCB) under the CHINT brand. It is mainly used for circuit protection in lowvoltage power distribution systems.
- Indepth Analysis of Model Parameters
Each character/number corresponds to the key specifications of the circuit breaker, with specific meanings as follows:
| Model Segment | Meaning Explanation | Fonction principale |
| NXM | Series code for CHINT molded case circuit breakers | Identifies the product category. The NXM series is a mainstream lowvoltage power distribution protection product of CHINT, featuring high breaking capacity and stable performance. |
| 250 | Frame rated current (Inm) | Indicates that the maximum rated current the circuit breaker shell can withstand is 250A. It means that under this “shell model”, releases with different rated currents (par ex., 160UN, 200UN, 250UN) can be adapted. |
| S | Breaking capacity grade | “S” represents the standard breaking type (the breaking capacity is usually 35kA; refer to the product manual for specific values). En outre, there are grades such as “H” (pouvoir de coupure élevé) et “L” (low breaking capacity). The higher the breaking capacity, the better it can safely cut off the fault large current. |
| 3200 | Pole number + Release type | The first digit “3”: 3 poteaux (suitable for threephase circuits, such as industrial motors and threephase power distribution); |
| The second digit “2”: thermalmagnetic release (the most commonly used type, which realizes overload protection through a “thermal bimetal sheet” and shortcircuit protection through an “bobine électromagnétique”); | ||
| The last two digits “00”: No accessories (par ex., no leakage protection, no auxiliary contacts, etc.. If it is “01”, it is equipped with auxiliary contacts; if it is “30”, it is equipped with leakage protection). | ||
| 200UN | Release rated current (Dans) | It is the core protection parameter of the circuit breaker, referring to the maximum continuous current allowed when the circuit is working normally. When the circuit current exceeds 200A for a long time (surcharge), the release will trip with a delay; if the current far exceeds 200A instantaneously (court-circuit), it will trip instantly to cut off the circuit. |
- Core Functions and Protection Characteristics
As a “safety guardian” of lowvoltage power distribution, its core role is to prevent the expansion of circuit faults. The specific protection functions include:
- Protection contre les surcharges
When the circuit current continuously exceeds 200A due to excessive load (par ex., motor stalling, simultaneous startup of multiple devices), le “thermal bimetal sheet” in the release will deform due to heat, pushing the mechanism to trip with delayed action (to avoid false tripping caused by shortterm overload), thereby protecting wires and equipment from damage due to overheating.
- ShortCircuit Protection
When a short circuit occurs in the circuit (par ex., direct contact between live wires, neutral wires/phase wires), and the current surges to hundreds or even thousands of amperes instantaneously, le “bobine électromagnétique” in the release will generate a strong magnetic field, which attracts the iron core to push the trip instantaneously. The circuit is cut off within 0.1 secondes, preventing equipment burnout, fire or electric shock accidents.
- Power Distribution Control
In addition to the protection function, it can also be used as a “switch” for normal circuits. Manual closing/opening can realize the onoff control of threephase equipment (par ex., moteurs, distribution boxes).
III. Scénarios d'application
Based on its characteristics of 3 poteaux, 200A rated current and standard breaking capacity, it is mainly used in lowvoltage threephase power distribution systems. Typical scenarios include:
Industrial workshops: Used as the main protection switch for threephase motors (par ex., 2030kW motors) and large machine tools;
Commercial buildings: Used as the main protection or branch protection for threephase power cabinets (par ex., outdoor air conditioner units, elevator power supplies) in shopping malls and office buildings;
Civil power distribution: Used as the threephase incoming main switch for highrise residential buildings and villas (if the incoming power supply is threephase), or as the protection switch for threephase central air conditioners and energy storage equipment;
Outdoor power distribution: Used for the lowvoltage side protection of street lamp control boxes and small distribution transformers (below 100kVA).
- Précautions d'utilisation
- Matching Circuit Parameters: Ensure that the rated voltage (usually AC 380V) and load current of the circuit do not exceed the specifications of the circuit breaker. Avoid the situation of “a small horse pulling a big cart” (par ex., using a 200A circuit breaker to protect a 300A load), which may lead to protection failure;
- Adaptation of Breaking Capacity: If the shortcircuit current of the power distribution system is large (par ex., near the transformer), it is necessary to confirm whether the “35kA breaking capacity” meets the onsite requirements. If not, select the “H” highbreaking type;
- Inspection régulière: During operation, regularly check whether the circuit breaker has heat generation or abnormal noise. After tripping, it is necessary to troubleshoot the fault (par ex., court-circuit, surcharge) and do not close the switch blindly;
- Professional Installation: It must be installed by certified electricians to ensure firm wiring (loose wiring is prone to heat generation and burnout). En outre, the 3pole wiring corresponds to the A, B, and C three phases, and must not be connected incorrectly.
 Contacteur,disjoncteur,onduleur solaire,compteur électrique,batteries solaires
Contacteur,disjoncteur,onduleur solaire,compteur électrique,batteries solaires















NH42-63-318x560.png)



